In the event you’ve been following this four-part collection, you then’ll know that we’ve already coated choosing your microphone, preparing your environment, and recording your voiceover. Now it’s time to complete issues off. And for this, we’ll be staying in Adobe Audition. It’s not your solely choice, and a number of the options famous right here will also be present in different purposes, so it’s best to have the ability to comply with this information even when you’re utilizing a special modifying instrument.
Adobe Audition is a strong audio editor, and like most of its kind, the extent of its characteristic set could make it intimidating to the newcomer (or perhaps a video veteran who’s by no means seen a spectral frequency show earlier than).
So earlier than we get all the way down to the specifics of modifying and cleanup, let’s check out the shows you’ll be utilizing in put up—waveform and spectral frequency.
Waveform
That is the only and most acquainted of the 2 and is time (x) plotted towards amplitude (y), with peaks indicating loudness. Simply as with the Ranges meter, that is measured in dBFS (decibels relative to full scale) with a most peak of 0dBFS.
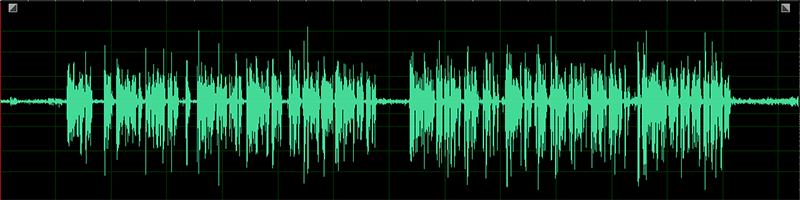
When you get to know the spectral frequency show a bit higher, you’ll most likely depend on the waveform view lots much less. However it’s nonetheless helpful to test for cases of audio clipping, or creating fade envelopes, or seeing how a lot headroom is likely to be obtainable for acquire or compression. However the chances are high that you just’ll spend most of your time with the waveform view minimized to offer the spectral frequency extra room, which you are able to do by dragging the horizontal divider up and all the way down to go well with.
Spectral frequency
At first look, the spectral frequency show (Shift+D) might be intimidating, but it surely’s really fairly easy. It plots time (x) towards audio frequency (y), and the colours are only a heatmap that reveals how loud the sound is at a given frequency. The brighter the colour, the louder the sound, so cross-referencing shiny and darkish areas towards the frequency axis will provide you with a surprisingly good concept of the sound being made.
Now, I’m not saying that you just’ll have the ability to learn phrases, however you’ll begin to pick among the extra apparent sounds, transients, and phonemes with a little bit of apply.
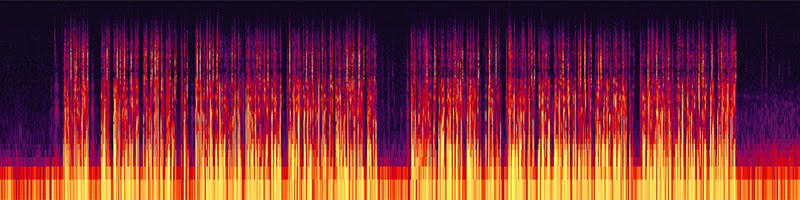
To supply a extra visible instance, listed here are the waveform and spectral frequency views of me saying “mmmmmmm” after which “tsssssssssssss”.

Buzzing lives within the decrease frequencies, so you may see my “mmmmm” is hottest between 200 and 500Hz, whereas the high-frequency sibilance of my “tsssss” seems to be brighter between the 4kHz to 10kHz mark. Compared, the waveform presents much less granular info, however you may nonetheless inform the place every sound begins and stops, in addition to their variations in amplitude.
Now we all know what we’re taking a look at. Let’s get to work.
Create your tough minimize
The very first thing to do together with your recording is to edit out the rubbish, leaving you with a single audio file that matches your script. Simply use the time selector (T) to spotlight the bits you don’t wish to maintain and delete them.
In the event you took my earlier recommendation and have ten seconds of silence/ambiance initially of your recording, go away this in place. And don’t fear an excessive amount of about timing at this stage, we will refine issues later.
Snapping
Audition permits “snapping” on the timeline by default, however you may toggle it with the S key or by clicking on the magnet icon on the high proper of the Editor panel. For essentially the most half, it’s best to go away snapping turned off as this may make it simpler to make correct guide alternatives. The exception to that is once you’re utilizing markers.
Marker choice
To keep away from shedding your home whereas modifying, use the M or * key to create a cue marker underneath your CTI (present time indicator, or playhead) to find the In level of your edit. Then discover your Out level and mark it in the identical style.
With snapping turned on, you’ll discover it a lot simpler to pick out the vary between the 2 markers, and it’s a helpful approach for making giant alternatives.
Alternatively, you may choose each of your markers within the Markers panel, by choosing them, right-clicking, and selecting Merge (or clicking on the Merge button). If you double-click on this new merged marker, the vary between your In and Out factors will likely be robotically chosen, and you may hit the Delete key twice to delete the marker then your choice.
If you’ve completed your tough minimize, reserve it as a brand new file to maintain it separate out of your unique recording.
Normalize your audio
The subsequent step is to normalize your recording. Hit F2, or click on on Results-Amplitude & Compression-Normalize (course of), and this may alter the acquire to raise (or drop) the audio’s loudest peak to the worth you set within the pop-up window.
Sometimes you may go away this at 0dB or -0.1dB, except you wish to go away some headroom for EQ (equalization) or a music mattress afterward, through which case, be at liberty to drop the ceiling a bit.
In case your recording ranges have been good, then normalization gained’t make a giant distinction and also you’ll solely see a slight raise throughout the waveform once you apply it. In case your ranges have been too low, then the distinction might be pronounced. And in the event that they have been too excessive (clipped) at any level, then normalization can have no impact in any respect, as a result of the clipped audio is already as excessive as it could go.
Normalize is certainly one of Audition’s many course of results, that are indicated by (course of) in drop-down menus. These are sometimes CPU-hungry results that require waveform evaluation, to allow them to’t be performed again in actual time and are completely utilized.
Laborious restrict
In the event you discover that your vocal ranges are being held again by a few pesky amplitude peaks, you’ve gotten a few choices. One in all these is to spotlight the troublesome peaks and selectively cut back their acquire utilizing the HUD (toggled with Shift+U). Dialing down the peaks will present extra headroom in order that Normalize has a larger impact.
Alternatively, you should use the Laborious Limiter to spice up your quieter sections, which is actually a compression impact. The Laborious Limiter isn’t a course of impact, so you may (and may) apply this utilizing the Results Rack panel, as that is non-destructive and means that you can alter settings later, and even toggle the impact on and off within the stack.
So as a substitute of choosing it from the Results drop-down, click on on the Add Impact button within the Results Rack (the triangle on the finish of the row) and choose Amplitude & Compression-Laborious Limiter. Preserve the Most Amplitude the identical as the worth you used to Normalize, and set the Enter Enhance to the worth you assume your quiet vocals want. The opposite values can keep at their defaults.
Play the audio whilst you make your adjustment, and watch the Enter and Output ranges on the Results Rack to see the distinction it’s making. As a tough information, it’s best to goal to have most of your vocals hanging across the yellow zone.
Keep in mind that the laborious restrict impact is a compressor, so it’s going to cut back your audio’s dynamic vary. You may undoubtedly overdo it, and it is probably not acceptable when you want a deeper vary of sounds from loud to quiet. (Compression is partially why adverts sound so loud.) To be taught extra about compression and its results, it’s best to definitely read this article.
Silence, please
The tolerance for background noise in voiceover recordings is often very low. Your editor will usually have to separate the observe into phrases to match the timing of what’s being stated to what’s being proven, and the ensuing silence between these clips will draw consideration to any background noise when the voiceover kicks in once more.
So we would like the house between our recorded vocals to be as near silent as doable. This may be achieved in numerous methods in Audition—like Adaptive Noise Discount and DeNoise—however I’ve at all times discovered the most effective outcomes come from the Noise Discount course of. However your mileage could differ, so be at liberty to test these options out.
Noise discount
To make use of the Noise Discount course of, you’ll want to give it a pattern of noise to work with, and for this reason you recorded these seconds of silence initially of your observe. And also you is likely to be considering, “does he imply room tone?” Which might be an inexpensive query, because it’s mainly the identical factor.
However whereas the recording is technically the identical, the target is the precise reverse. Tone is one thing you file so you may add it to the edit to make ADR sound prefer it occurred in-situ. Noise is one thing you file so to establish and take away as a lot of it as doable.
It would sound counter-intuitive, however use the spectral frequency show to wash up your noise pattern first. Search for transient noises like mouse clicks, keypresses, or breath, and take these out till you’re left with a bit of unpolluted, fixed background noise.
Spotlight this with the time selector and open the Noise Discount impact utilizing Cmd/Ctrl+Shift+P. Within the window that opens, hit the Seize Noise Print button to let Audition know that that is the noise you wish to take away, then Choose Whole File, and Apply.
The method will take a second to work, and it gained’t take away every little thing in a single go, as a result of Adobe has correctly chosen to set a much less aggressive profile because the default. As an alternative, it’s best to test the audio preview to guarantee that your first move hasn’t induced undesirable ringing or distortion results in your vocals (recognized within the enterprise as house monkeys).
In case your voice sounds positive however you may nonetheless hear some background noise, then give it a second move utilizing the identical noise print. You don’t need to get the gaps between your phrases wanting completely black, so don’t fear when you can nonetheless see darkish purple noise in your spectral frequency show.
Why DeNoise is likely to be a more sensible choice
The DeNoise impact is dynamic, so it’s higher at responding to altering background noise, like a airplane travelling overhead, or your aircon turning on and off. Its settings are easy and also you set it to concentrate on particular areas utilizing the Course of Focus sample buttons. So that you would possibly wish to give this one a shot when you discover that Noise Discount falls quick.
Nevertheless, in case your background noise is so dangerous that the noise discount course of can’t repair it with out distortion, simply get as shut as you may whereas conserving your vocals clear and we’ll deal with this manually.
A observe on reverb
Reverb is a tough factor. As a result of it’s a delayed reflection of your individual voice, it hides itself within the unique audio and is virtually not possible to take away with out harm. And the place voice is anxious, we’re extraordinarily delicate to synthetic modifications.
There are a number of reverb removing options (a few of which aren’t low-cost) together with one which’s constructed into Audition (and Premiere Professional). However my (admittedly not in depth) expertise with them means that the advantages are outweighed by the distortion they introduce.
So far as I can inform, de-reverb instruments work higher with extra echoey reverb (longer “tails”) as a result of the mirrored sound is extra discrete. However this isn’t a situation you’re more likely to expertise with VO recording (and is likely one of the the explanation why we put a lot effort and time into preparing the recording environment).
If you end up with audible reverb in your recording, your choice is likely to be to go away it sounding pure and ship a pattern to your editor to see in the event that they assume it’s usable. If it’s happening high of a music mattress, you’ll be stunned at how a lot you may get away with.
Breath noise and gaps
You should use brute drive to take away background noise and breath sounds out of your vocals just by highlighting them and utilizing both the HUD (Shift+U) to dial them down, or choosing Silence from the Results menu. However this may create a distractingly abrupt shift, particularly if the observe comprises audible background noise.
Making a fade envelope preset is a extra refined strategy. To do that, spotlight an space that you just wish to silence and choose Results-Amplitude & Compression-Fade Envelope (course of).
Develop the waveform view to offer your self some room, and zoom in in your choice. Examine the Spline Curves choice within the Impact-Fade Envelope pop-up, then click on on the yellow line within the waveform view to create keyframes initially and finish of your choice. Then create two further keyframes adjoining to those and drag them all the way down to the bottom of the waveform show in order that it seems to be just like the picture beneath.

Earlier than you hit the Apply button, take a second and save this as a preset so you may rapidly apply it to future recordings.
When you’ve utilized the impact as soon as, you may streamline the method by working by way of your recording, highlighting the areas you wish to silence, and hitting Cmd/Ctrl+R to immediately apply the final impact to your choice. So do that now.
De-Essing
Relying in your voice or microphone, you might not just like the sibilance in your recording. It’s doable to coach your self to scale back this whereas talking, however a extra rapid resolution is to get Audition to repair it for you.
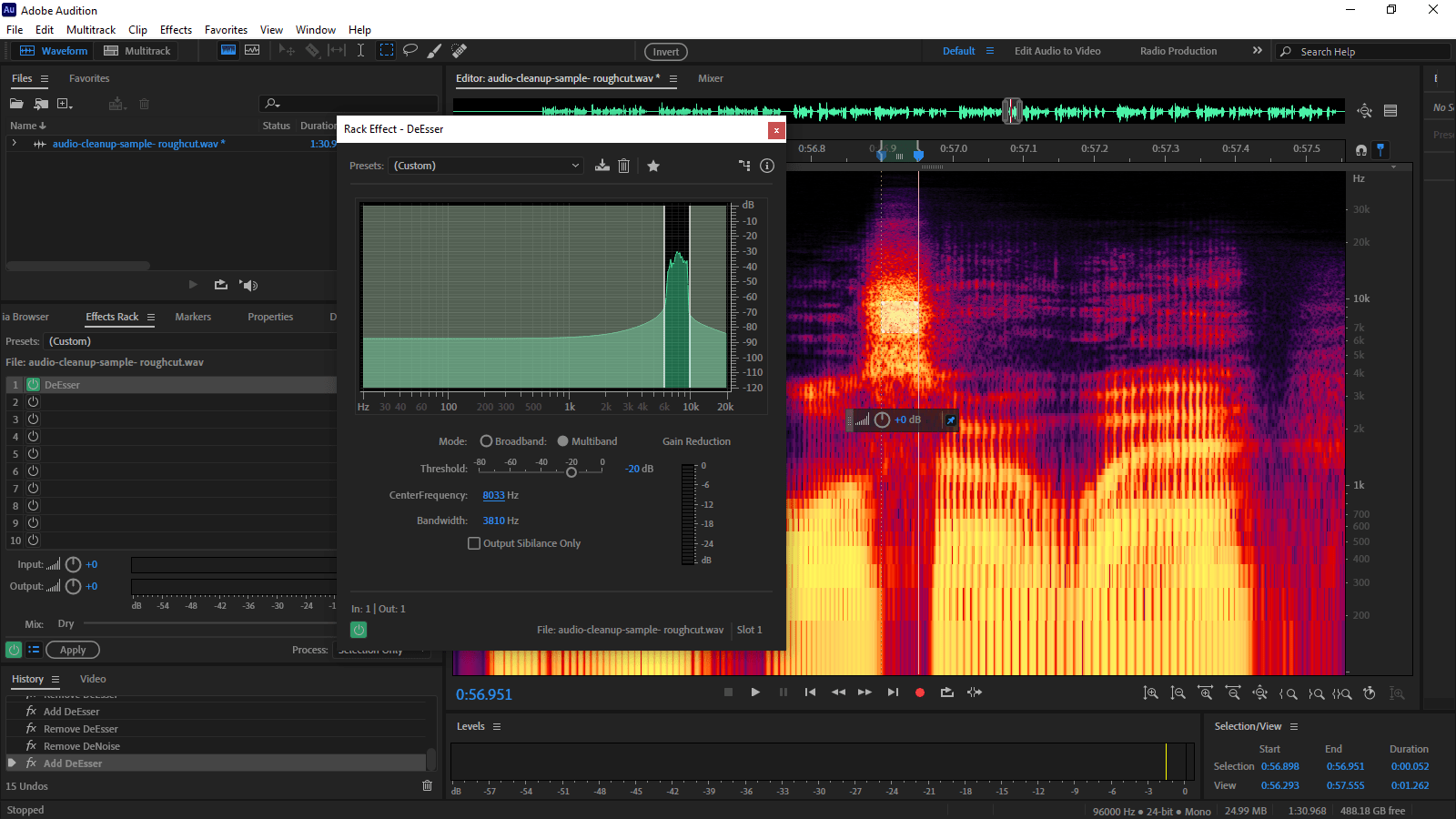
Begin by discovering certainly one of your loudest cases of sibilance and use the marquee choice instrument (E) to spotlight its hottest half within the spectral frequency show. Flip preview looping on utilizing Cmd/Ctrl+L, and use the following obtainable slot in your Results Rack so as to add Amplitude & Compression-DeEsser.
When the Rack Impact-DeEsser window opens, faucet the Spacebar to play your choice and also you’ll see it clearly within the impact show (see beneath). Cease the preview and drag the CentreFrequency worth to maneuver the default choice into this area, then alter the Bandwidth values to refine the vary. Decreasing the Threshold worth will enhance the quantity of DeEssing utilized, however use it sparingly and test the way it sounds in different areas of your recording.
Eradicating pops/plosives
Even with a pop filter in your mic, it’s seemingly that you just’ll hear an occasional thump in your vocals brought on by air hitting the pickup once you use plosives (P and B sounds).
The excellent news is that these are very easy to take away as a result of they sit within the sub-200Hz area. So once you hear one, use the spectral frequency show to search for a hotspot on this space. It won’t be that apparent, so use your ears to isolate it.
If you discover it, merely use the marquee choice instrument (E) to spotlight the area between 0 and 200Hz and hit Delete. Even with male vocals, it’s best to discover that this takes it out with out leaving an audible hint.
Mouth noise (clicks)
And whereas we’re on the subject of eradicating undesirable transients, it’s best to maintain an ear open for the worst of all of them—sticky mouth sounds. (Even when you have been well-hydrated through the recording, I can assure these clicks will present up someplace.)
With a bit apply, you’ll begin recognizing these within the spectral frequency show earlier than you even hear them. They manifest as sharp needle-like shapes within the mid to excessive frequencies, and also you’ll discover about twenty of them within the instance beneath—although not all of them will likely be audible.

If there’s a strategy to take away these robotically with out affecting the remainder of your vocals, I’m afraid I haven’t discovered it. Luckily, the Spot Therapeutic Brush (B) does a unbelievable job of stripping these off-putting noises out of your recording.
Zoom in on the spectral frequency show till you may clearly see these transients, then resize the comb instrument in order that it comfortably exceeds their width utilizing the [ and ] keys. Maintain down Shift to lock the comb to the vertical, then merely draw a single stroke over the offending noise.
If you let go, the Spot Therapeutic Brush will strip the transient out by portray adjoining noise excessive—precisely just like the equal instrument in Photoshop. It’s time-consuming however actually satisfying. Right here’s a fast earlier than/after so you may see what I imply. (In the event you can’t hear the distinction, then it’s best to most likely get some different headphones.)
And now that you just’ve used it for this, now you can apply the identical approach to every kind of sound removing, like birdsong or smartphone notifications. Simply paint over them within the spectral frequency show, and also you’ll be stunned at how usually it really works.
<h3>The Equalizer
Within the fingers of a talented sound engineer, equalization—or EQ—to make use of its cooler nickname—is an extremely great tool. Utilizing daring changes, it could perform as a high- or low-pass filter to dam out hum or hiss, whereas refined tweaks can enhance the readability and character of your recording.
As a result of we’ve already addressed the noise and ranges of our observe, EQ at this stage is an aesthetic moderately than corrective measure. And it’s most likely value having a chat together with your editor earlier than you go including EQ—they may have one thing particular in thoughts, and should favor to work together with your file because it now stands (through which case, you may skip to the mastering stage).
You would possibly recall that I discussed my mic—the sE Z3300a—has a shiny high finish, however is fairly flat throughout the remainder of the spectrum. So I’ve created a preset that helps to fill out the low finish whereas de-emphasizing the sibilance in my voice. Keep in mind these microphone frequency response charts from part one? They are often helpful right here.
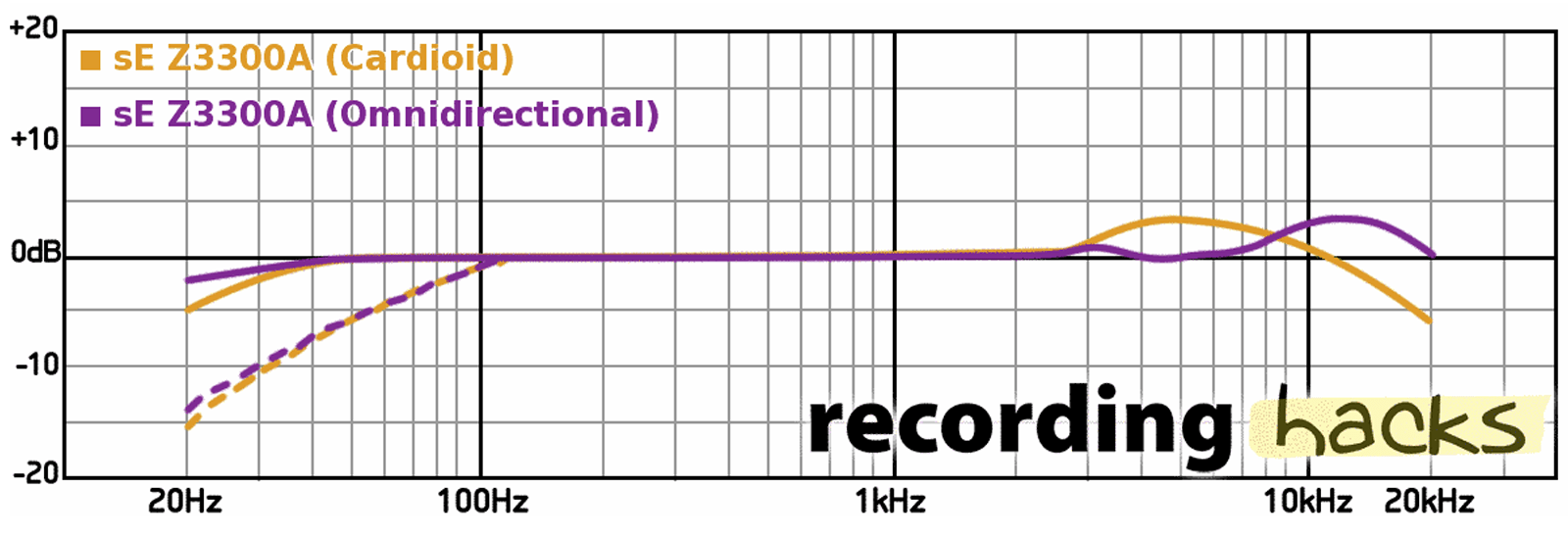
You may, in fact, do that totally by ear, however referring to the frequency response graph can provide you a baseline to begin from. And there’s nothing stopping you from creating a number of presets.
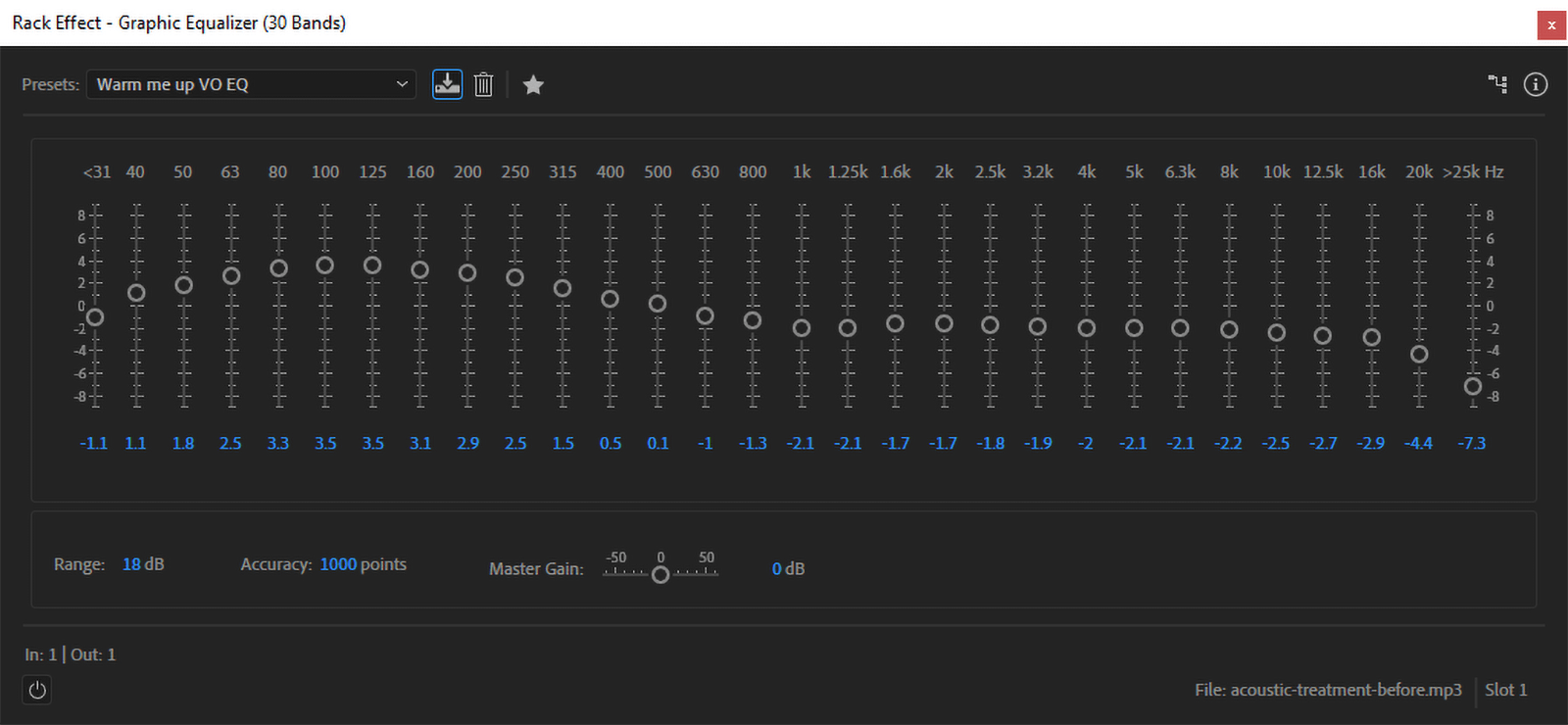
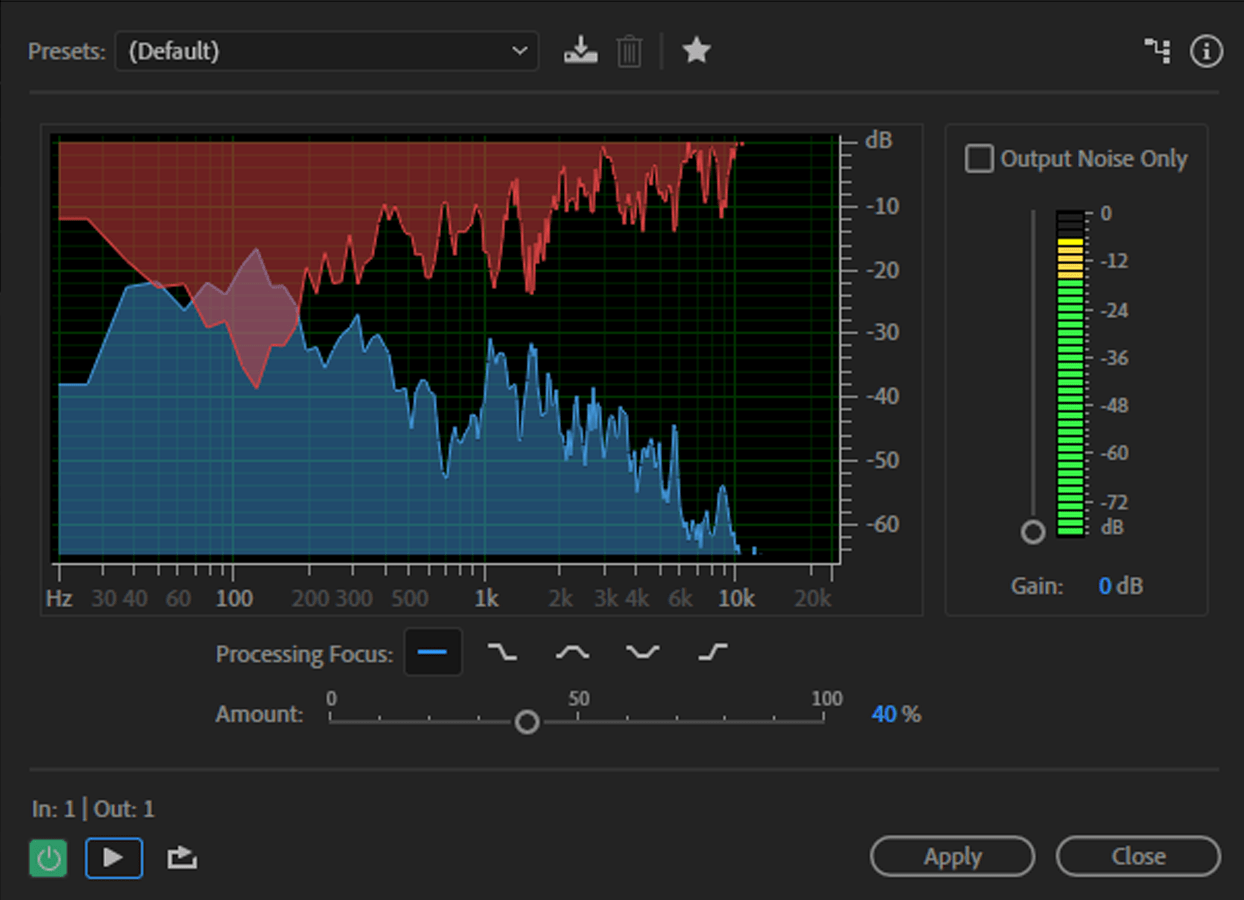
To use an EQ, choose the Filter & EQ-Graphic Equalizer (30 bands) within the subsequent obtainable slot in your Results Rack. Then dial within the settings that reverse any undesirable traits of your microphone—like an overly-bright top-end—earlier than including changes to offer your vocals the tone and shade that you really want.
EQs will stack in your Results Rack, so you may create a baseline EQ to flatten your microphone’s frequency response—consider it as a technical LUT, however in your microphone—after which drop one other EQ on high for character. And if you end up doing this lots, then be sure to save them as presets for straightforward choice.

This isn’t going to show your $60 Behringer C1 right into a $8.5K Brauner VMA, however with a bit work, an EQ can add character to your vocals that your microphone could have missed. Right here’s a pattern of how my EQ preset sounds:
Earlier than including EQ
After including EQ
As at all times, your ears ought to be your information when experimenting with EQ, however generally it helps to have a map. Like this one from ProducerHive, which illustrates key frequency ranges and the results they will have on the tip consequence.
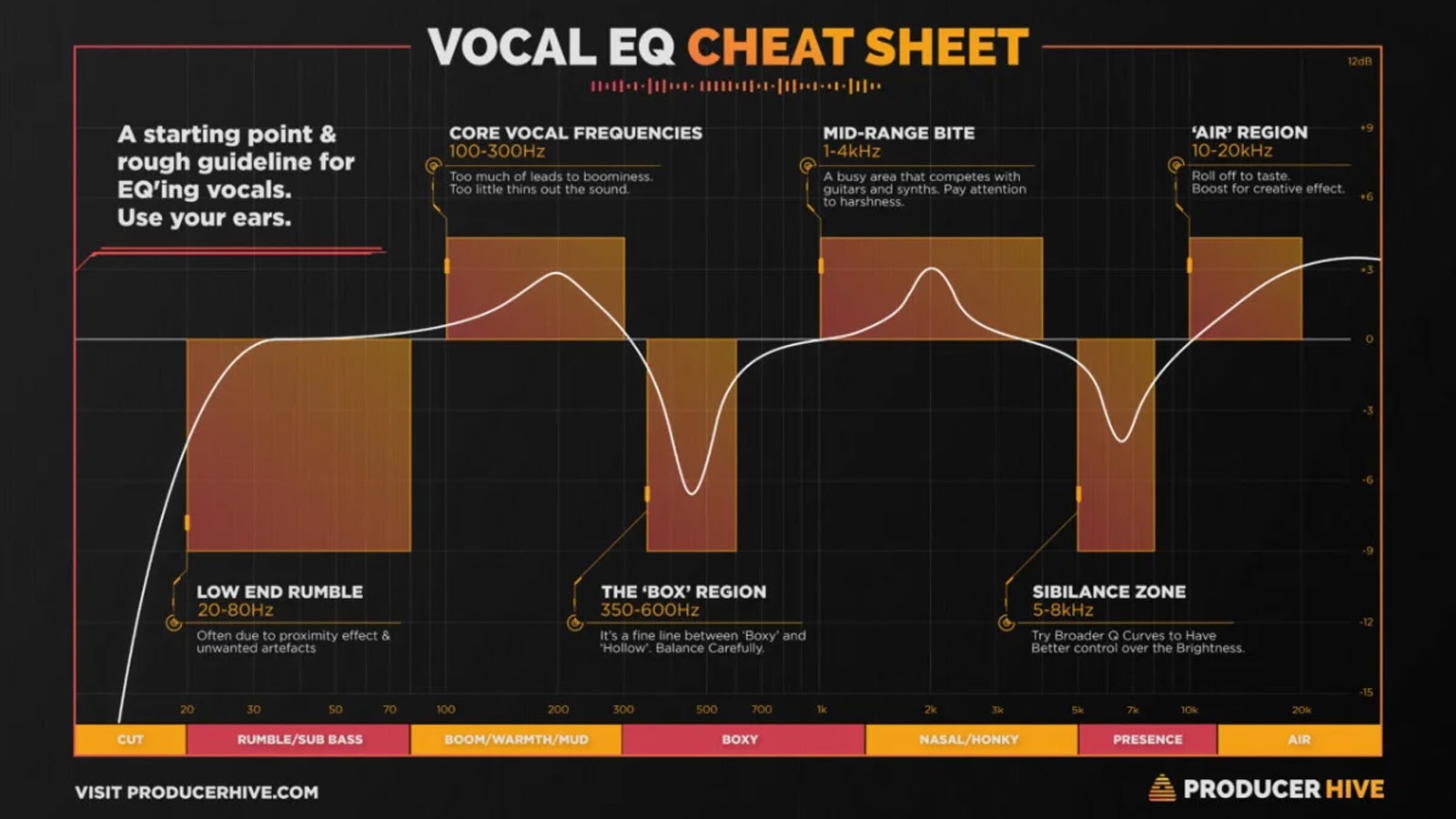
If you’ve acquired your audio sounding simply the way you need it to. It’s time to complete it off.
Render your rack
Any results you’ve gotten in your Results Rack must be rendered, in any other case they gained’t make it into the exported file (Audition will warn you about this). So hit the Apply button to course of the stack.
This can apply all of the lively results to your observe, and can clear all the results from the stack—even people who have been disabled. You may undo this course of, however the modifications will likely be everlasting as soon as the file is saved. (Which is why we made that backup initially.)
Mastering your audio
A fast phrase about broadcast loudness requirements. Proper now, your voiceover might be not broadcast-compliant, which means that it doesn’t meet with native loudness requirements like EBU R128, or ATSC A/85.
However that’s okay. You may go forward and export it as-is, as a result of your voiceover is only one element of the ultimate manufacturing, so mastering for broadcast can wait till all the opposite elements are within the combine.
However when you’re curious, you may test your recording by including the TC Digital Loudness Radar to your Results Rack. (That is additionally obtainable inside Premiere Professional.)
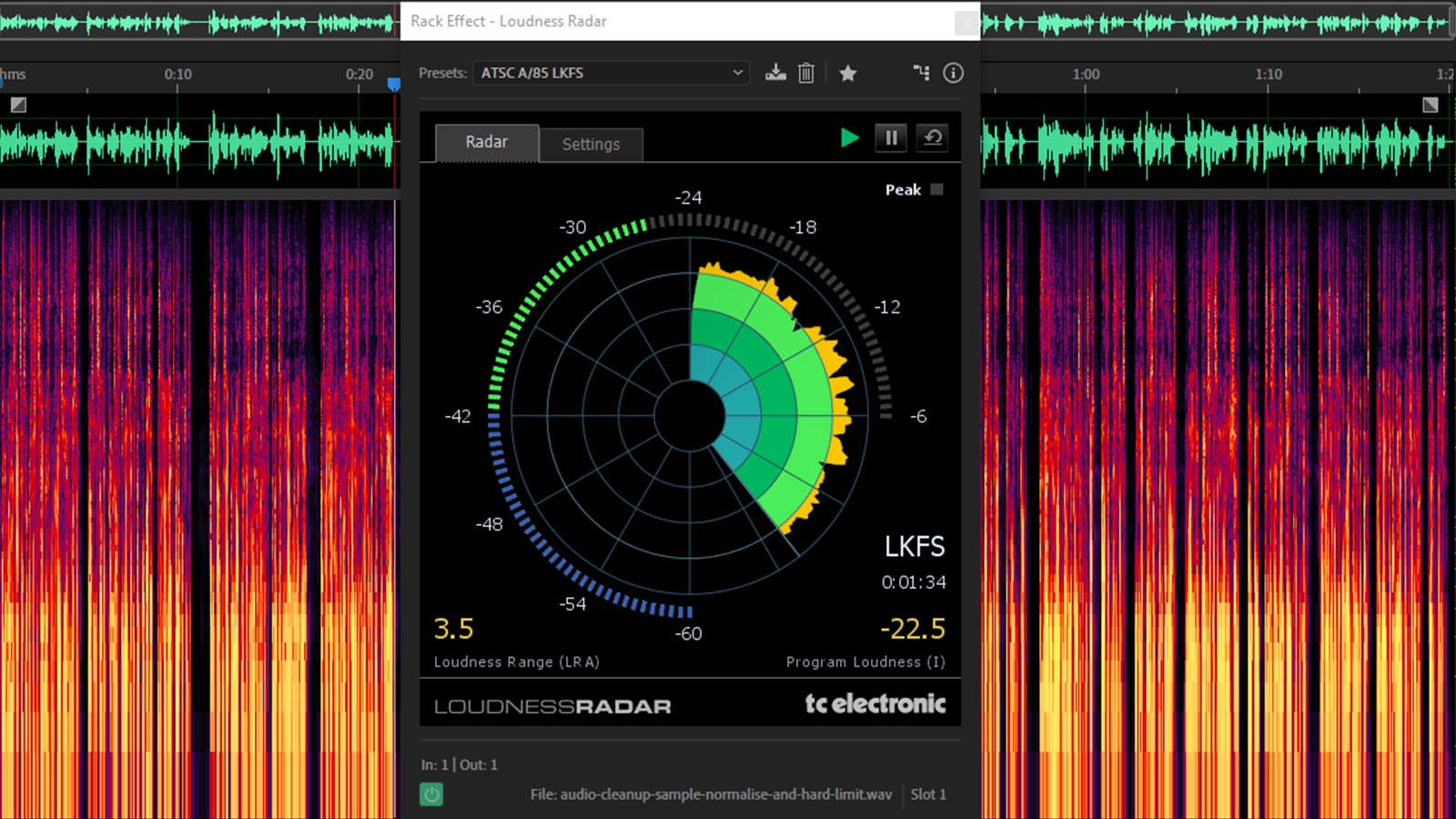
With this loaded, you may select from numerous broadcast requirements from the presets drop-down, after which preview your audio to see the way it matches up.
LUFS/LKFS
Broadcast requirements use a barely completely different measurement scale referred to as Loudness (Ok-weighted) relative to Full Scale (LKFS) or Loudness Models relative to Full Scale (LUFS). For sensible functions, these are the identical factor.
In contrast to dBFS, LKFS and LUFS are a greater measurement of how we understand sound loudness as a result of they characterize values over time and so they think about dynamic vary.
Match Loudness
If, nonetheless, you’ve been requested by your editor to satisfy a selected commonplace together with your voiceover, you are able to do this utilizing Audition’s Match Loudness panel (Alt+5). Simply drag your file(s) into the panel, decide the printed commonplace you want from the Match To dropdown, and hit the Run button.
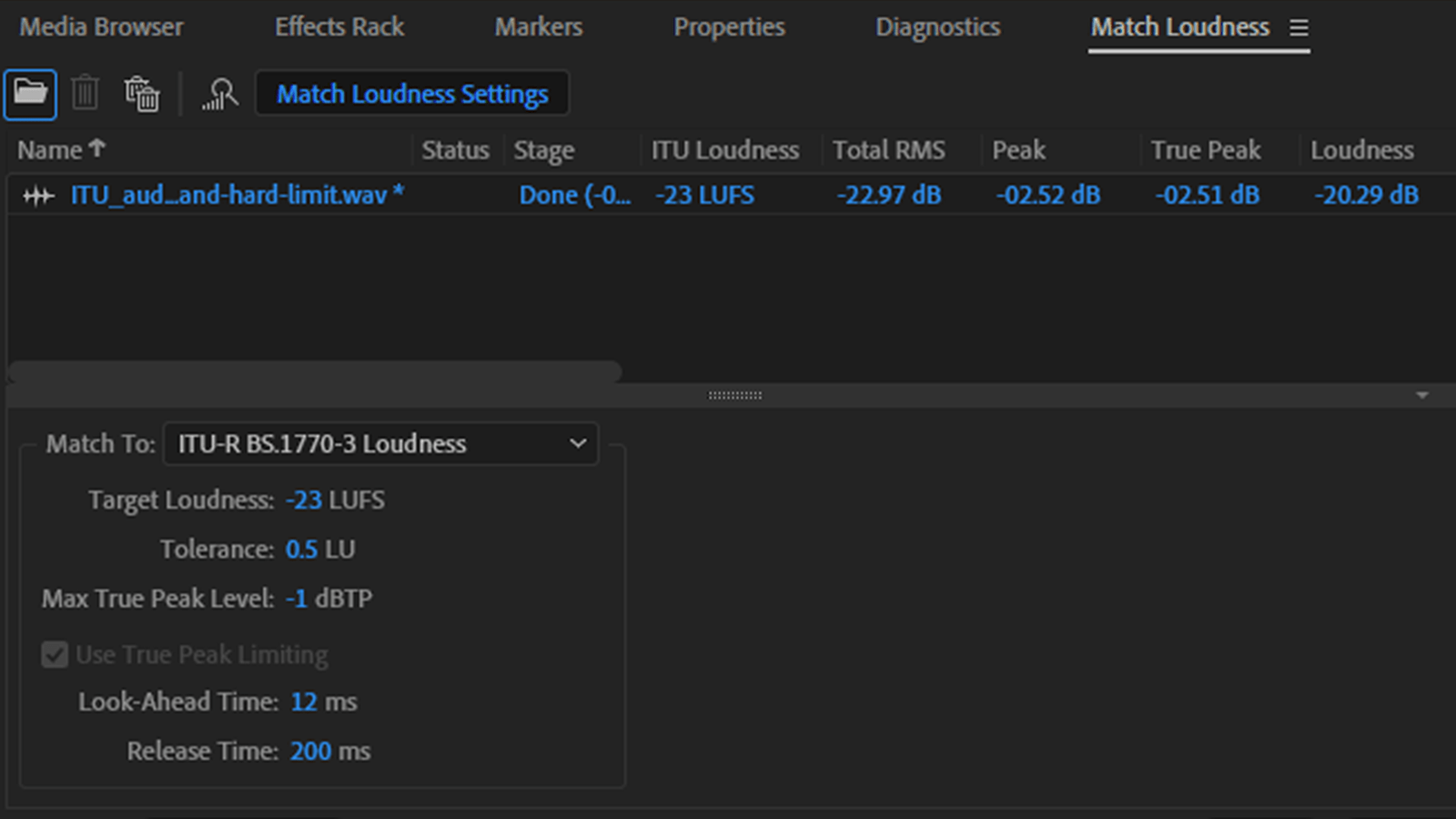
In the event you simply wish to run the audio evaluation, you may toggle the Export perform off earlier than hitting Run, and this will provide you with a breakdown of the audio file and the modifications that will likely be made when you commit. For extra info on broadcast audio specs, take a look at Jeff Hinton’s article.
Choose your export format
There’s a bunch of export codecs obtainable however, in your mastered audio, the frequent commonplace is uncompressed WAV, whether or not you’re on PC or Mac. Simply decide the pattern price and bit depth settings that correspond to your recording settings, hit the OK button, and your newly-minted voiceover is able to ship to your editor.
In conclusion
Like I stated initially of this collection (when you can bear in mind again that far), that is certainly not the one strategy to get to the place you’re going in the case of voiceovers. So when you assume I’ve missed something, or want to add some methods of your individual, throw a remark within the part beneath. Thanks for sticking with me all the best way to the tip, and good luck together with your vocal profession!















Leave a Reply